- Home
- Solutions
- Solutions
- Engineering Solutions
- Anchor Systems
- Design Guidelines for anchor systems
- Seismic Design - Anchor baseplate
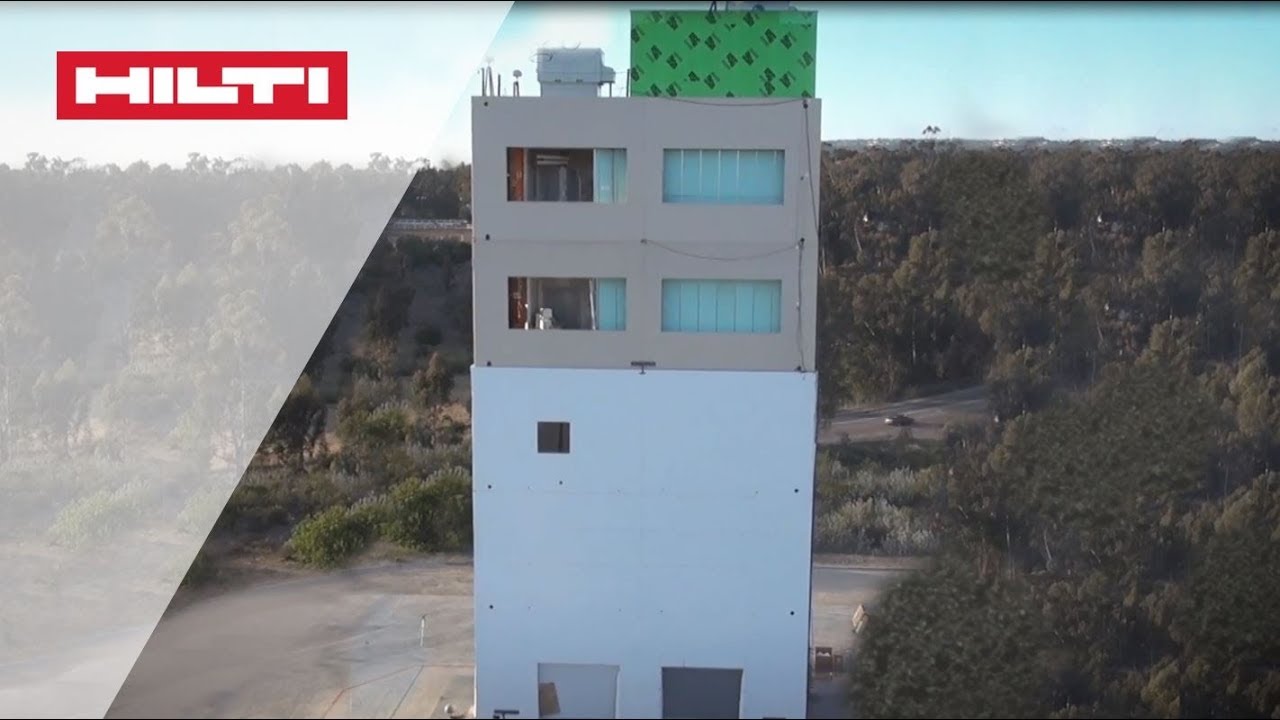
HOW TO ANCHOR A BASEPLATE IN SEISMIC AREAS
Fastening systems for earthquake zones

Earthquakes are much more common than we realize, happening every day all over the world.
Not only can they bring a great cost of life, but they can also do great damage to buildings and the economy.
All this can be limited by good seismic construction design and specification.
It’s important to include seismic design for both non-structural and structural elements of a building, as research shows that non-structural systems suffer the largest damage in commercial buildings during an earthquake.
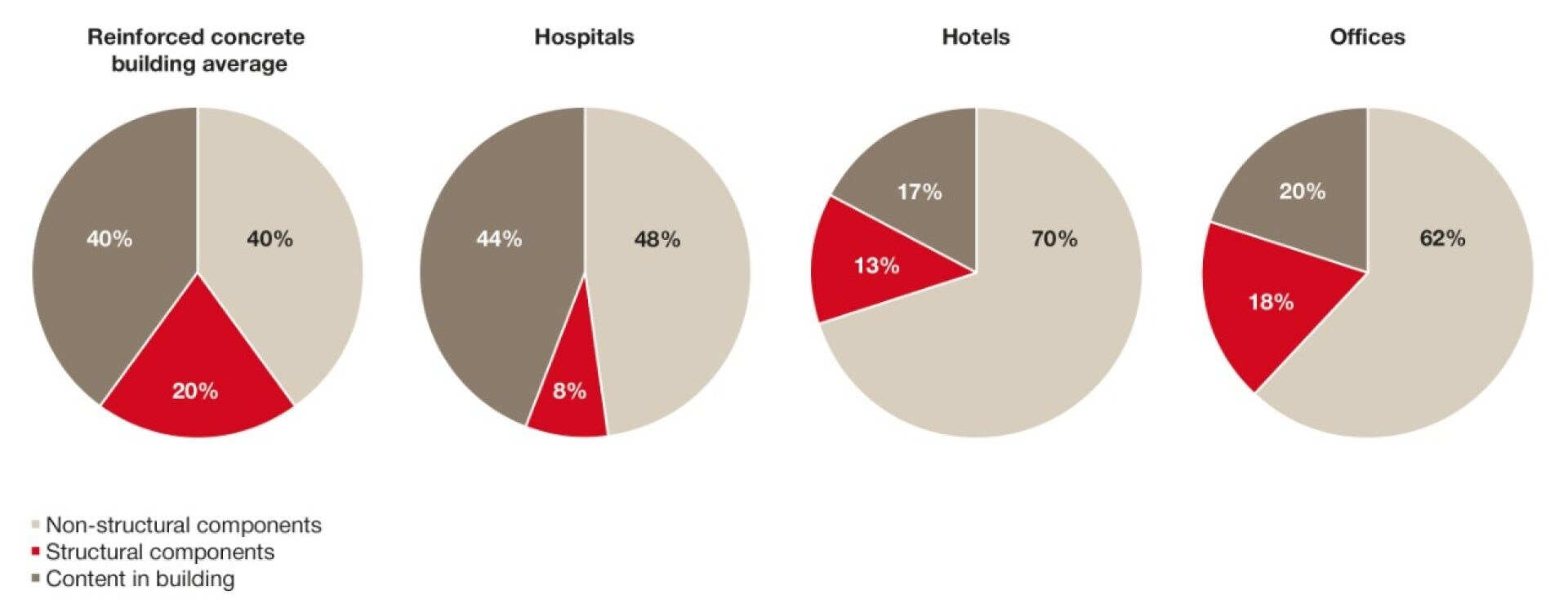
Repair Costs Resulting From a Seismic Event
How anchors behave in an earthquake
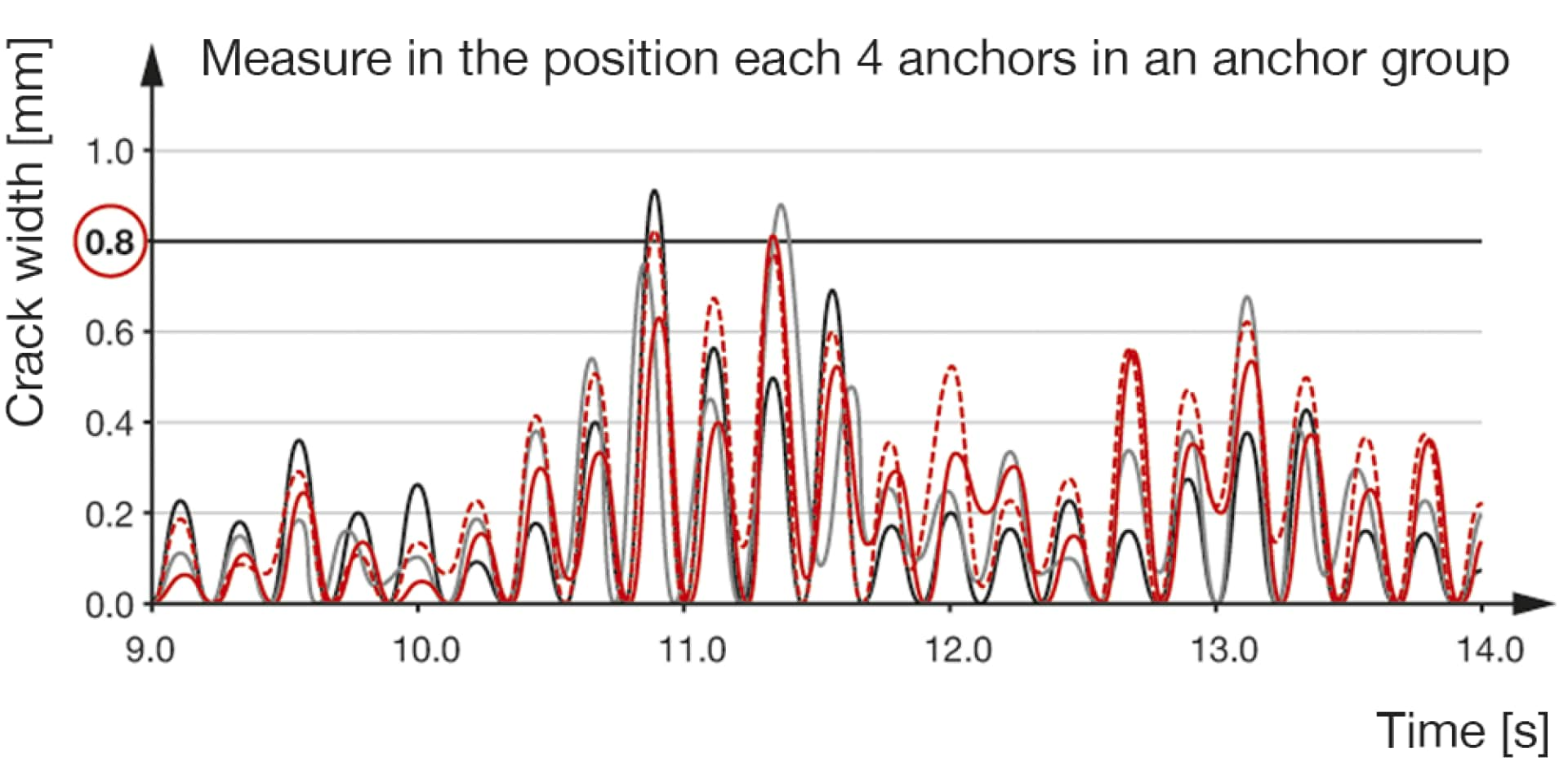
Compared to static events, seismic load conditions can have a significant effect on anchor performance and capacity.
The crack width can be up to 0.8 mm during seismic according to ETAG001, supported by extensive research.
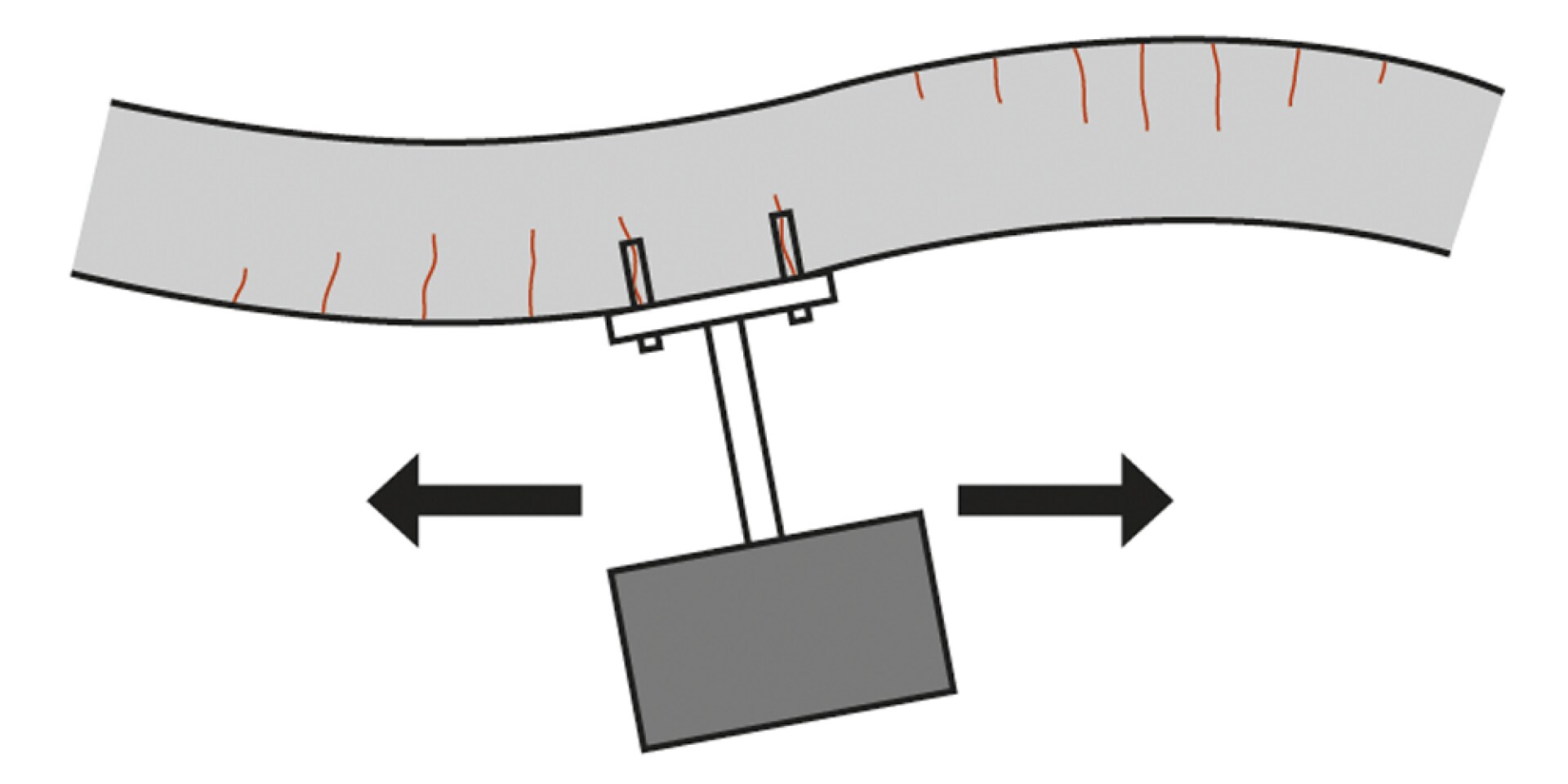
High cyclical loads due to inertia forces in the multi-directions.
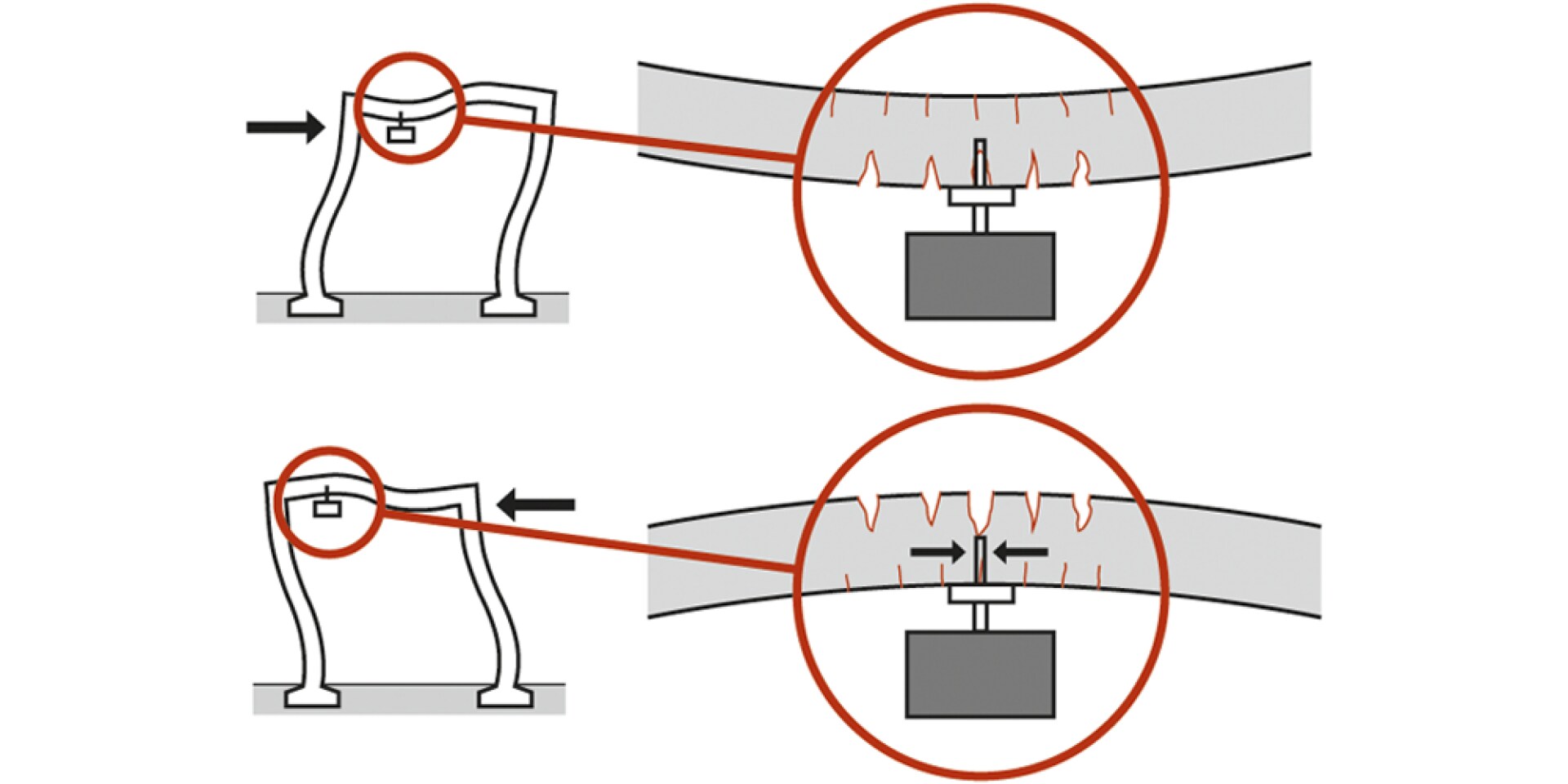
Cracks open and closing dramatically during earthquake. Loaded anchor tend to slip out under such crack cyclic pattern.
Understanding the issues in seismic areas
How Hilti anchors comply with seismic codes
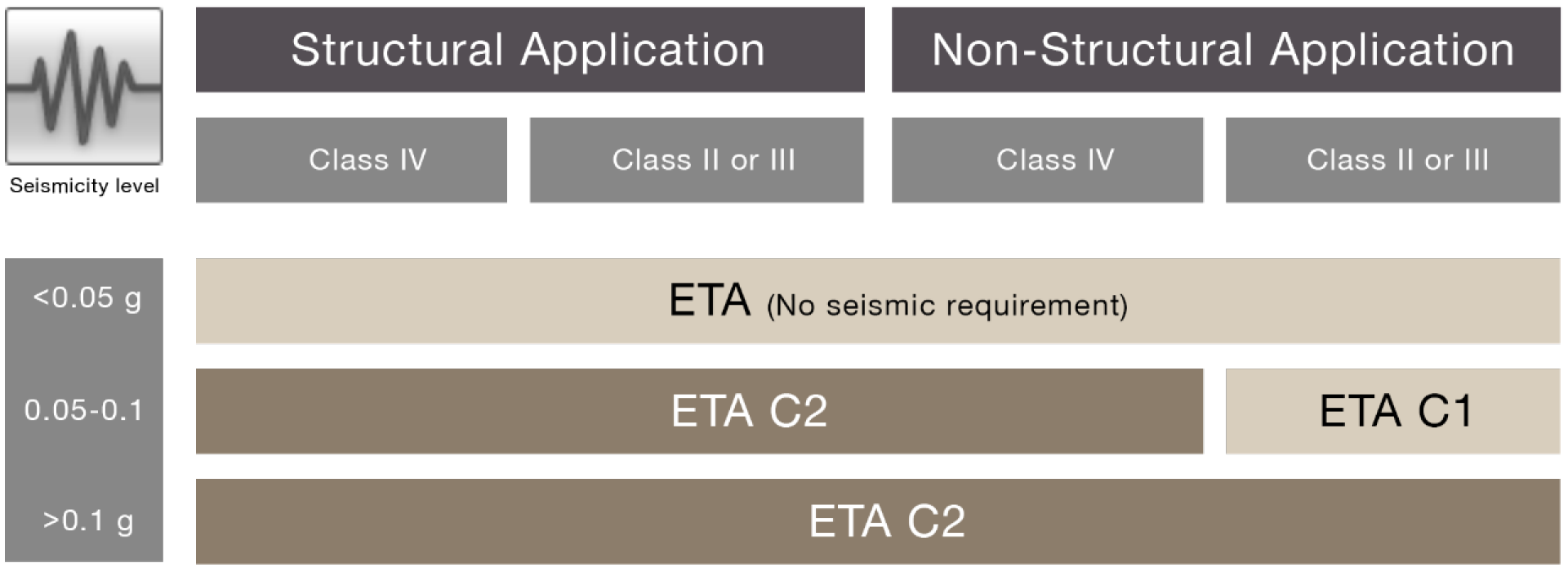
There are already codes in place to determine which anchors should be used in seismic areas.
EOTA TR045 clearly states most of the applications only allow the use of category C2 anchor systems for seismic areas.
At Hilti we produce a range of anchors, which are code compliant and fit seismic performance category C2.
Anchor fasteners with an ETA Qualification

How do I design anchors for seismic areas

Our Field Engineers can provide you with the technical support you need for your anchor design – contact our Engineering Department for more details.
Or, you can use our Hilti PROFIS Anchor software for your anchor fastener design, and generate relevant design reports for for specifications.
Our PROFIS Anchor software performs seismic calculations according to EOTA TR 045. This provides three solutions for anchoring base plates in seismic areas:
Capacity design
The anchorage is designed for the force corresponding to the yield of a ductile component, or if lower, the maximum force that can be transferred by the fixture or the attached element.
Elastic design
The fastening is designed for the maximum load assuming an elastic behavior of the fastening and of the structure.
Design with requirements for anchor ductility
This design for ductile steel failure requires an anchor classified as ductile. This approach is also applicable only for the tension component and some provisions need to be observed in order to ensure that the cause of failure is steel failure.
We’ve also introduced Hilti SOFA method into PROFIS Anchor design software, to cover the scope beyond EOTA TR 045 and help you to find engineering solutions based on Hilti research results.

