LEGAL REQUIREMENTS FOR FIRE PROTECTION
European regulations for fire resistant building design

HOW TO BUILD FIRE ESCAPE AND RESCUE ROUTES
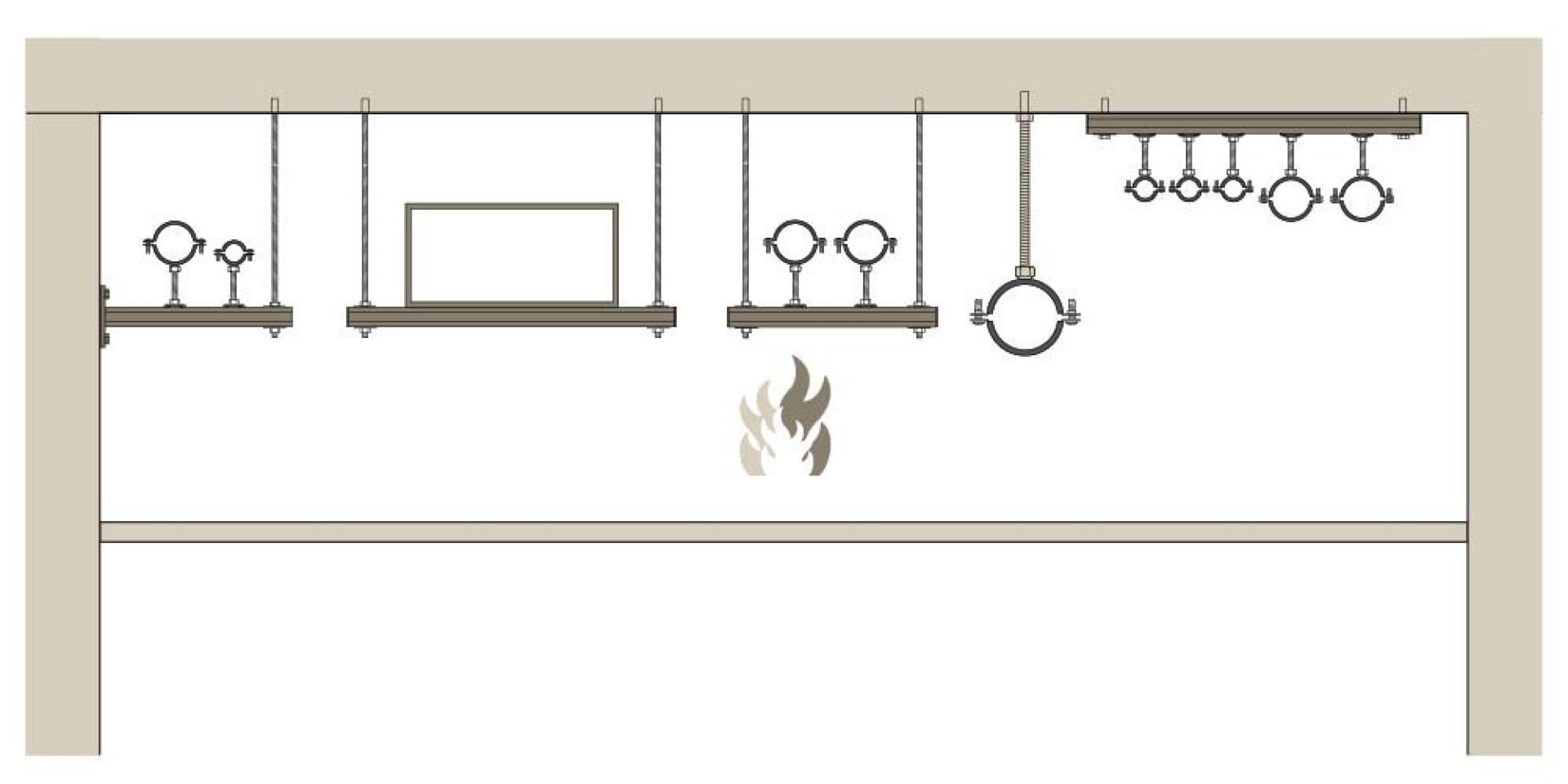
One of the most important considerations when designing for fire protection is giving people inside the building enough time to get out if there’s a fire.
The German guidelines MLAR [4] (current version 11/2005), describe how to keep escape routes free and for how long in the event of a fire.
MLAR [4] key messages include:
- For fire rated suspended ceilings, the required fire resistance must be guaranteed in the event of a fire coming from above and below the ceiling.
- Special requirements must be observed for modular support systems, installed between the structural ceiling and the suspended ceiling.
Share
